Access your logs
Back to home
On this page
Activity logs 
Changes to your environments, such as deployments, cron jobs, and code or variable updates, are each logged as activities. You can access the logs either in the Console or using the CLI:
- Open the project you are interested in.
- From the Environment menu, select an environment.
- Click a recent activity from the activity feed or click All to see the complete history.
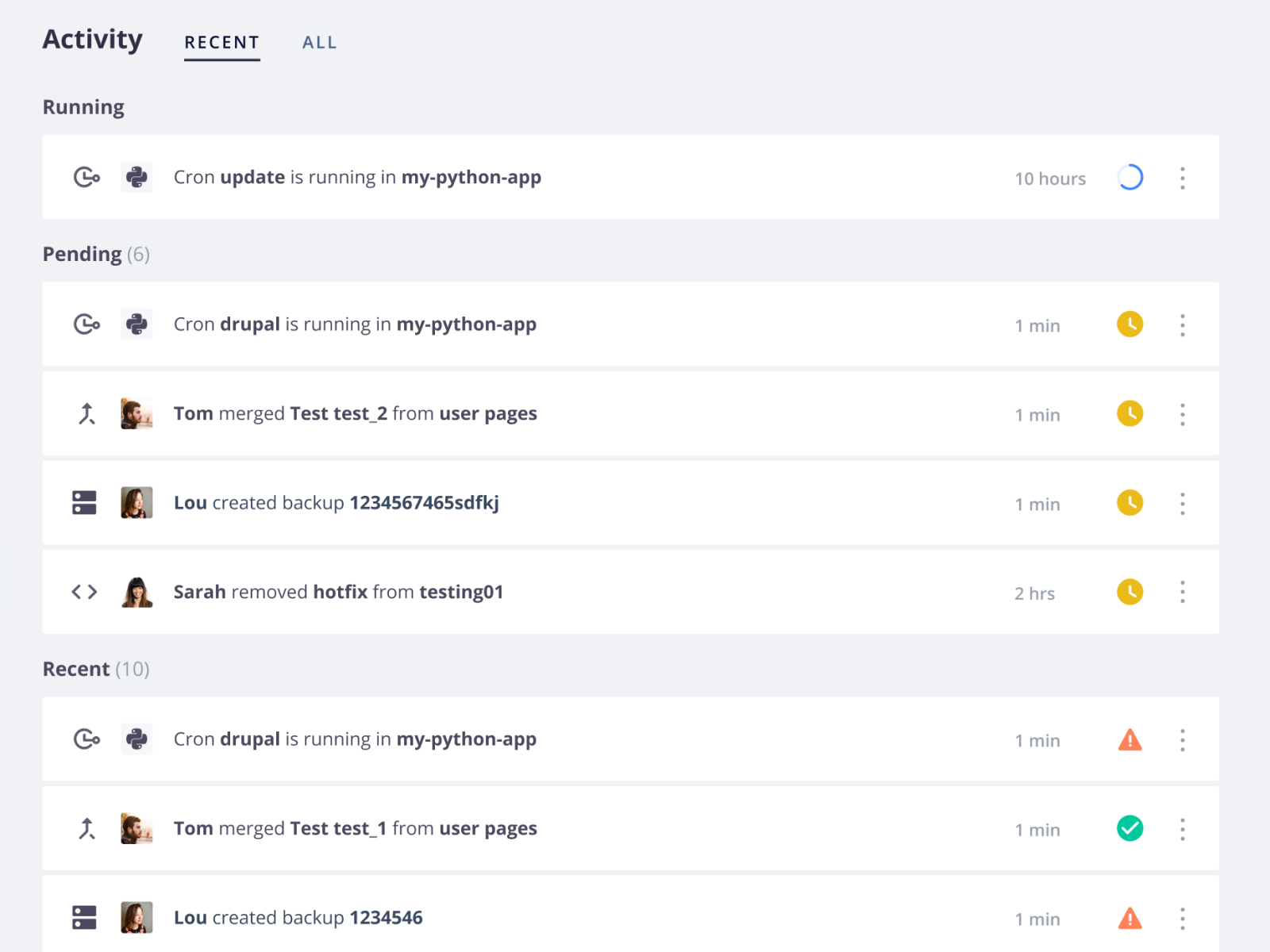
-
Get a list of activities by running
upsun activity:list -e ENVIRONMENT_NAMEPass the
--startflag to get activities from a specific date in the past. -
To see details about the activity’s state and timing, run
upsun activity:get ACTIVITY_IDWhere ACTIVITY_ID comes from the list in step 1.
-
Get a log of any given activity by running
upsun activity:log ACTIVITY_ID
If a running activity is stuck, you can cancel the activity.
Sharing activity logs 
When trying to identify and resolve failures, it can often help to have another person’s perspective. Troubleshoot collaboratively by sharing the logs of specific activities.
To share a log, open the log and click Copy URL.
Share specific lines in the log on clicking the line number. To select multiple lines, hold Shift. After selecting multiple lines, hovering on the next unselected line gives you the amount of time that passed between the selected lines.
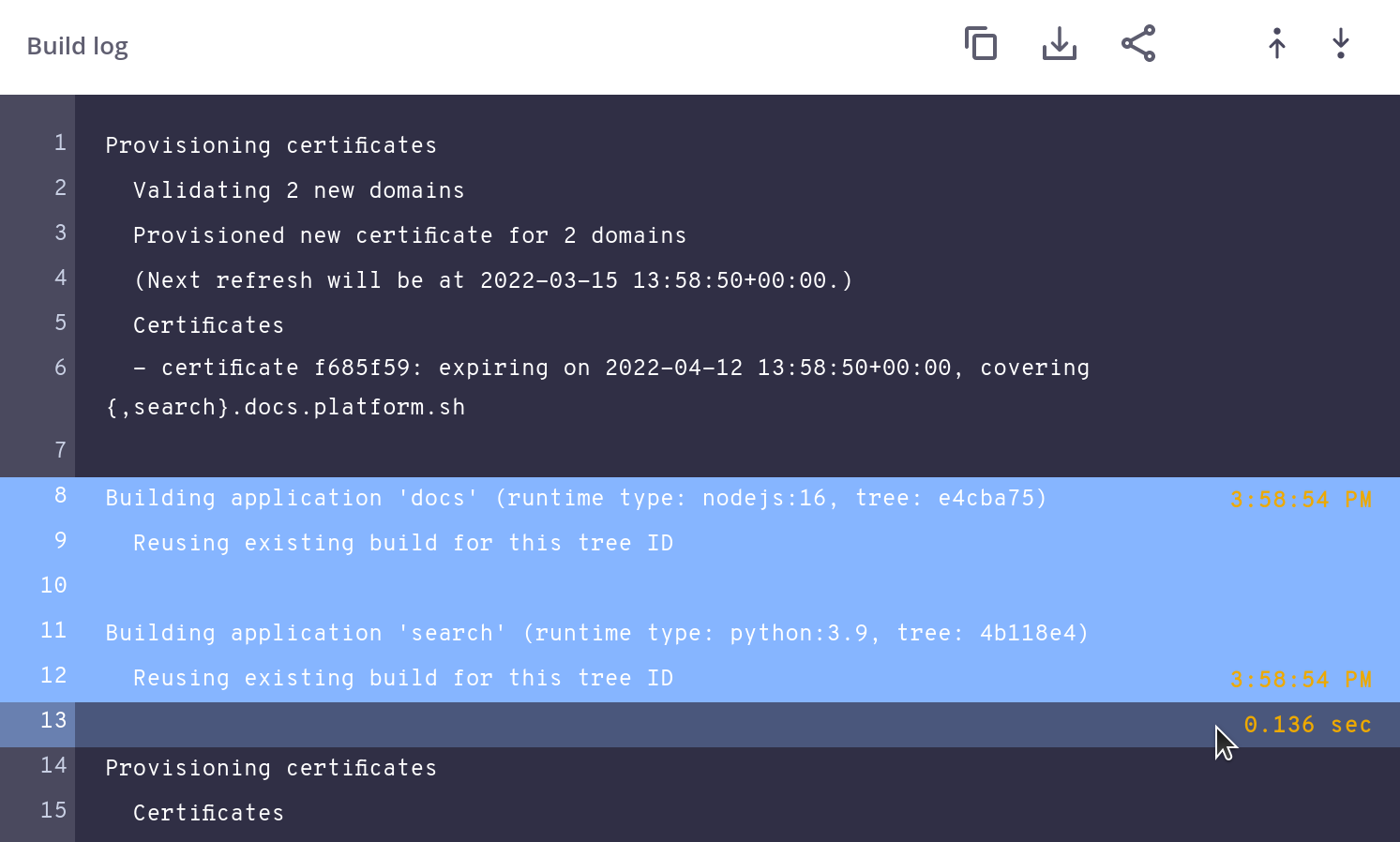
Container logs 
Events that occur within an app container are logged within that container. The logs can be written to, but you should do so only with standard logging mechanisms. If your app has its own logging mechanism, use it to write to a dedicated logs mount.
To access the logs of various types of events:
Use the upsun log command and specify the type of log you want.
For example, to get the access log, run:
upsun log -e ENVIRONMENT_NAME accessTo get other logs, just replace access with the type of log.
To view more lines, use the --lines flag.
-
Access the container by running
upsun ssh -e ENVIRONMENT_NAME -
Change to the right directory by running
cd /var/log. -
Read the desired log, such as by running
tail access.log.
All log files are trimmed to 100 MB automatically. If you need larger logs, set up a cron job to upload them to third-party storage. See an example of uploading logs to Amazon S3 from Contextual Code.
Types of container logs 
| Type | Always present | Description |
|---|---|---|
access |
Yes | The raw access log for the nginx instance running on the container. It doesn’t include requests that are redirected or cached by the router. |
app |
Yes | All log messages generated by the app including language errors and exceptions. |
cron |
No | The output of cron jobs. Only exists after a cron job has run. |
deploy |
No | The output of the deploy hook. Only exists after a deploy hook has run. |
dns |
Yes | All DNS queries made by processes in the container (such as the app and cron jobs). |
error |
Yes | nginx-level errors that occur once nginx has fully started such as HTTP errors for missing directories and excluded file types. |
nginx/error |
No | All nginx startup log messages. Only useful when debugging possible nginx configuration errors. Not currently available using the upsun log command. |
php.access |
No | A record of all requests to the PHP service. See PHP access record format. |
post-deploy |
No | The output of the post_deploy hook. Only exists after a post_deploy hook has run. |
syslog |
Yes | General system-wide logs. |
PHP access record format 
The formatting of php.access.log is determined by the PHP settings.
To determine the format, run the following:
upsun ssh cat -n /etc/php/PHP_VERSION-zts/fpm/php-fpm.conf | grep "access.format"You get a response such as the following:
Connection to ssh.eu.platform.sh closed.
access.format = "%{%FT%TZ}t %m %s %{mili}d ms %{kilo}M kB %C%% %{REQUEST_URI}e"See what each value in this string means.
Timezones 
UTC is the default timezone for all logs.
